Streamlining GitHub Project Uploads: Automating Multiple Project Uploads with Bash Scripting
Introduction
Uploading multiple projects to a GitHub repository can become tedious, especially when managing different branches manually. Developers often spend valuable time navigating through folders, initializing repositories, committing changes, and pushing them to GitHub, all while ensuring consistency and accuracy across branches.
This blog post will explore a solution to streamline this process using a bash script. By automating the uploading of multiple projects to a GitHub repository in different branches, developers can save time, reduce errors, and maintain a more organized workflow.
Setting up the Bash Script:
#!/bin/bash
username_or_organization=""
repository_name=""
# Run Node.js script to extract folder names
folders=$(node -e '
const fs = require("fs");
const dirs = fs.readdirSync(".")
.filter(file => fs.statSync(file).isDirectory());
console.log(dirs.join("\n"));
')
# Set IFS to newline character only (To handle folder names with spaces correctly in the loop)
IFS=$'\n'
# Loop through folder names
for folder in $folders; do
# Sanitize folder name to use as branch name (Replace space with _ character)
branch_name=$(echo "$folder" | sed 's/ /_/g')
echo # This echoes an empty line for readability
echo "📁 Processing folder: $folder (Branch: $branch_name)"
echo # This echoes an empty line for readability
# Change directory to the project folder, exit if failed
cd "$folder" || { echo "Failed to change directory to $folder"; exit 1; }
# Initialize git repository
git init
# Add all changes, exit if failed
git add . || { echo "Failed to add changes to the index"; exit 1; }
# Commit changes with folder name as commit message, exit if failed
git commit -m "Committing changes for $folder" || { echo "Failed to commit changes"; exit 1; }
# Rename branch with the branch name we generated, exit if failed
git branch -M "$branch_name" || { echo "Failed to create branch $branch_name"; exit 1; }
# Add origin
git remote add origin git@github.com:$username_or_organization/$repository_name.git
# Push the branch to origin, exit if failed
git push -u origin "$branch_name" || { echo "Failed to push branch $branch_name to origin"; exit 1; }
# Go back to the parent directory
cd ..
done
# Reset IFS to its default value
unset IFS
The bash script provided serves as a powerful tool for automating the process of uploading multiple projects to a GitHub repository. Let's delve into how it works:
The script is designed to iterate through folders within the current directory, treat each folder as a separate project, and upload it to a GitHub repository in a dedicated branch.
Variables:
username_or_organization: Specifies the GitHub username or organization where the repository resides.
repository_name: Indicates the name of the repository on GitHub.
Script Execution Process:
Let's walk through the execution process of the bash script:
Iteration through Folders: The script iterates through each folder found within the current directory.
Folder Extraction: The script utilizes a Node.js script to extract folder names within the current directory. This ensures that each project folder is processed sequentially.
Sanitizing Folder Names: Folder names are sanitized to comply with branch naming conventions. Spaces are replaced with underscores to ensure compatibility with Git.
Repository Initialization: Git repositories are initialized within each project folder.
Adding Changes and Committing: All changes within the project folder are added to the index and committed with a message indicating the folder name.
Branch Creation and Pushing: A new branch is created for each project, with the sanitized folder name as its name. The changes are then pushed to the respective branch on the GitHub repository.
Let’s use it!!
Open https://github.com/new in the browser and create a new repository.
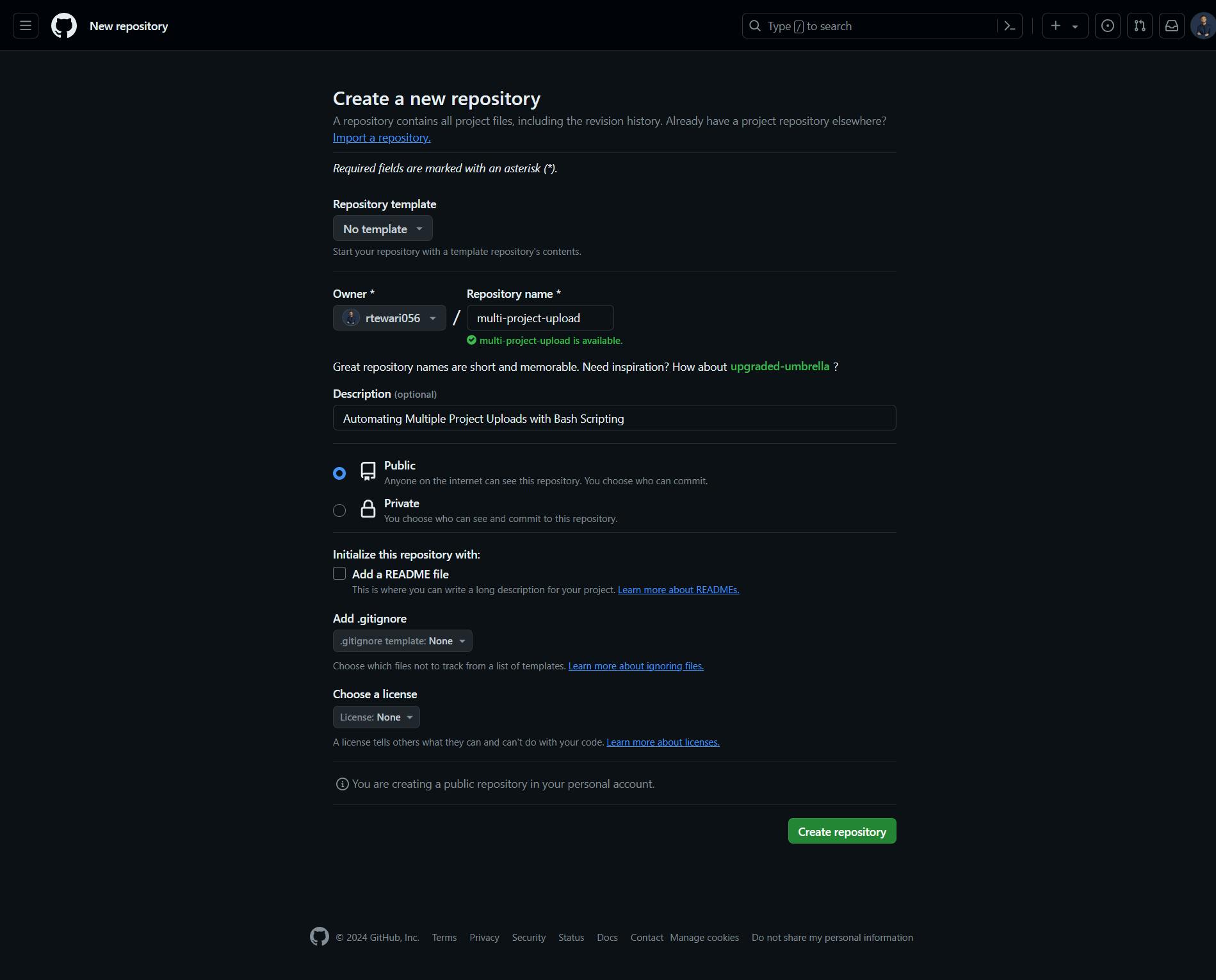
Save the provided bash script as
auto-upload.shwithin the root directory of your projects and change the value of the variables with actual values.username_or_organization="rtewari056" repository_name="multi-project-upload"Now run the bash script using your preferred terminal of choice.
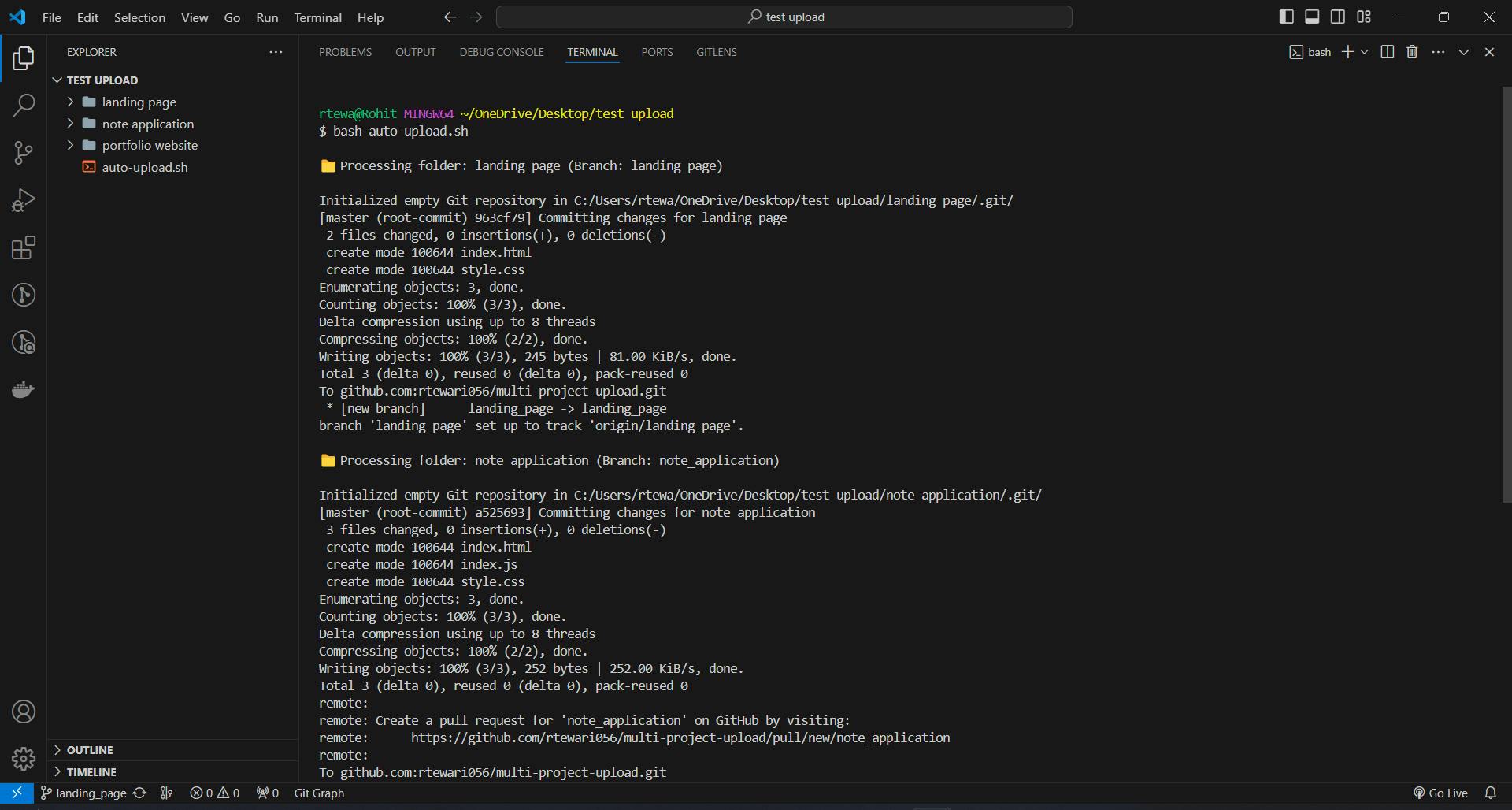
As you can see the projects were uploaded to the GitHub repository.
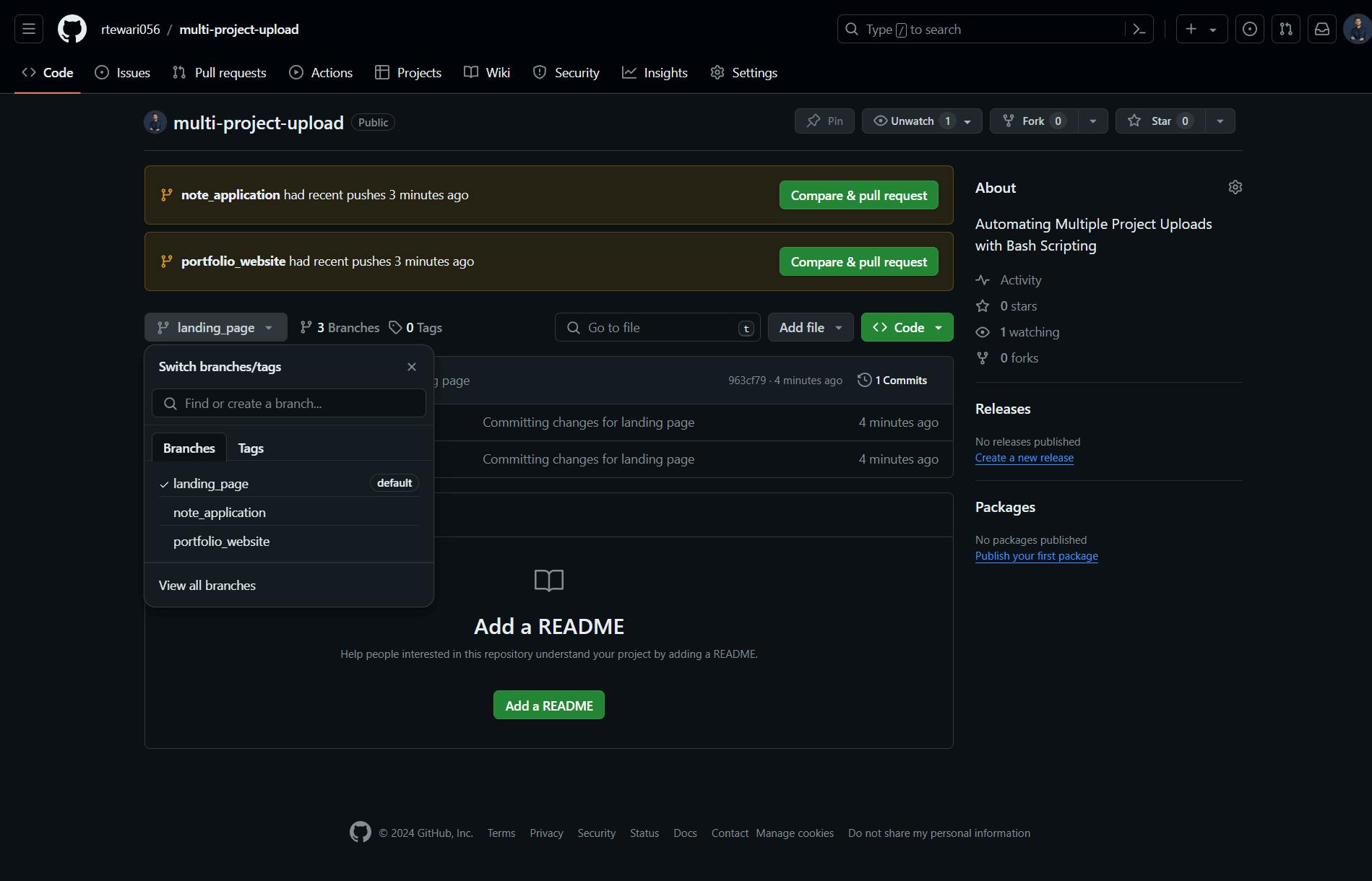
That’s all! Now we have a script capable of uploading single/multiple projects to GitHub in a dedicated branch.
Conclusion:
Automating the process of uploading multiple projects to a GitHub repository using a bash script offers numerous benefits for developers. By eliminating manual intervention and streamlining the workflow, developers can allocate more time to coding and innovation.
Encouraging developers to explore and customize the provided bash script for their specific needs can further enhance productivity and efficiency in project management.